Today, 1st June 2021 the Clean Air Zone in Birmingham was launched. The city follows in the steps of London and Bath in a bid to reduce pollution in the city. The Class D Clean Air Zone (CAZ) applies to all vehicles, which do not meet the minimum emissions standards of Euro 6 for diesel and Euro 4 for petrol vehicles.

What Euro classification is my vehicle in?
| Vehicle newly registered from: | |
| 31 December 1992 | Euro 1 |
| 1 January 1997 | Euro 2 |
| 1 January 2001 | Euro 3 |
| 1 January 2006 | Euro 4 |
| 1 January 2011 | Euro 5 |
| 1 September 2015 (majority of vehicles) | Euro 6 |
Restrictions now apply to all road networks inside Birminghams A4540 Middleway Ring Road, apart from the actual ring road itself. The CAZ is in force all the time – 24 hours a day, seven days a week, which includes bank holidays.
Drivers will not need to pay the daily fee and the council will not pursue enforcement until 14th June – giving drivers fair notice.
Putting Lives at Risk:
According to the World Health Organisation, dirty air has been putting lives at risk for a long while, with an estimated 4.6 million people dying each year as a direct result of ambient (outdoor) air pollution. Around 91% of the world’s population lives in places where air quality levels exceed WHO limits.
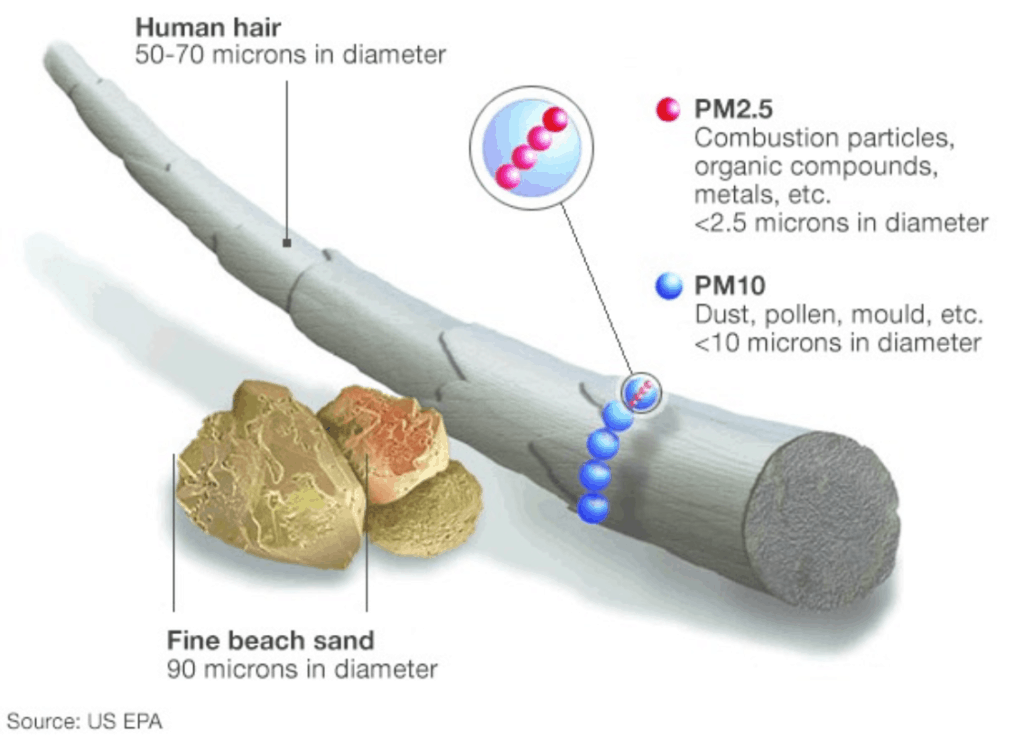
Top Three Causes of Air Pollution:
Particulate Matter – (PM-PM10 and PM2.5)
Particulate Matter is generally categorised on the basis of the size of the particles (for example PM2.5 is particles with a diameter of less than 2.5µm). PM is made up of a wide range of materials and arise from a variety of sources. Concentrations of PM comprise primary particles emitted directly into the atmosphere from combustion sources and secondary particles formed by chemical reactions in the air.
PM derives from both human-made and natural sources (such as sea spray and Saharan dust). In the UK the biggest human-made sources are stationary fuel combustion and transport. Road transport gives rise to primary particles from engine emissions, tyre and brake wear and other non-exhaust emissions. Other primary sources include quarrying, construction and non-road mobile sources. Secondary PM is formed from emissions of ammonia, sulphur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen as well as from emissions of organic compounds from both combustion sources and vegetation.
Oxides of nitrogen – (NOX)
All combustion processes in air produce oxides of nitrogen (NOX). Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and nitric oxide (NO) are both oxides of nitrogen and together are referred to as NOX. Road transport is the main source, followed by the electricity supply industry and other industrial and commercial sectors.
Ozone (O3)
Ozone is not emitted directly from any human-made source. It arises from chemical reactions between various air pollutants, primarily NOX and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), initiated by strong sunlight.
The formation can take place over several hours or days and may have arisen from emissions many hundreds, or even thousands of kilometres away.
Improving Air Quality:
Clean Air Zones will help improve air quality, so will other initiatives such as moving towards green, sustainable ways to heat a home, which includes burning wood on Ecodesign Ready stoves, improving home insulation, avoiding using outdated, ineffective appliances, stopping burning on open fires, ceasing coal use and much more. Hydrogen is also a path to reducing pollution. It’s already being introduced and will eventually replace natural gas to heat homes in the UK. You can learn more about hydrogen as a heating source here.







